There are a variety of important terms for understanding alternative investments. You can find more information about some of the most important ones here.
A
An investor or entity that meets certain criteria defined by the SEC. These are generally based on income, assets, or knowledge. Accredited investors have greater access to alternative investments.
After Repair Value (ARV) is a term used in private credit opportunities for real estate. These are loans for “fix and flip” projects. The ARV is a measurement of the loan value against the projected value of the property after it has been renovated and sold on the market.
This is often expressed as a percentage. For example, a $100K loan for a property that is projected to be worth $200K after repairs would be a 50% ARV.
Generally speaking, the higher the ARV, the greater the risk. A higher ARV% means that there is a lower margin of safety between the capital being provided and the estimate of what the property will be worth once renovations complete. Since estimates are never perfect and market conditions can change, that margin of safety is important for increasing the chances that the investment principal is preserved.
An appraisal is a process of trying to assess the “fair” market value of an asset. Both the process and how “fair market value” is determined can vary between appraisers.
This makes it an inexact estimate that typically relies on comparable sales. What is “comparable” is also an inexact science, explaining some causes of potential variance. It is also possible – especially in alternatives – that some assets have very few or no good comparisons to determine a value.
For example, in late 2023 Rally launched an offering for Mickey Mantle’s childhood home. You could compare that to other real estate sales in the same area, but what makes it special is Mickey Mantle having grown up there, not how many bedrooms there are. Even if there were other sales of famous athlete’s childhood homes, they’re likely few and far between (both in terms of time, market conditions, and geography) making them poor points of comparison as well.
The appraised value is basically the result of an appraisal process. It’s an estimate of what an asset would be worth if it were sold in the present market conditions.
This generally describes the total value of holdings a company is managing. This can be the value of cash, as well as the total appraised value of assets like real estate or shares of private companies.
At a high level, many investment platforms list this figure to roughly describe the total size of investors’ accounts across the platform. A company that has a higher AUM is generally using this to imply positive things about their size, success, and trustworthiness.
There are many different fee structures in alternative investing. One of the most common is to charge a fee based on the assets under management. In this model, the investment company will typically take a percentage of the AUM as a yearly fee.
For example, a $1M investment with a 1% AUM fee is $10,000.
Watch out: These fees can also grow or change as the appraised value of the investment changes. Not every platform or opportunity will do this. How this works is typically buried within the offering documents. The sponsor or investment platform will almost never explicitly highlight this for you.
Also, the process for appraisals varies between platforms. In some cases, the reappraised value will be based on an internal assessment. This gives the company an obvious potential conflict of interest.
B
Not all investment platforms play by the same set of rules and restrictions. One meaningful distinction is whether or not they are a broker-dealer.
Broker-Dealers have to register with the SEC and face various regulatory restrictions. One of the most important restrictions is only providing investment opportunities to investors they are suitable for. In practice, this means you should expect to complete a suitability questionnaire before being able to participate in offerings on the platform.
Becoming a broker-dealer can also affect the type of offerings a company can provide. For example, farmland investing platform AcreTrader became a registered broker-dealer in March of 2023. In an announcement to investors, they summarized the impact as:
“Greater variety of offering types and structures to invest in!”
After this the platform started hosting sponsor-managed (as opposed to AcreTrader-managed) farmland offerings for the first time.
C
Cap rate is a financial performance metric commonly used in real estate investments. It’s the net operating income (NOI) divided by the property purchase price. This is not an estimate of cash flow or yield as the NOI does not include all expenses. This includes the mortgage cost!
A higher cap rate is generally better as it offers more potential for cash flow from the investment. However, it’s still important to exercise reasonable discretion here. These figures can be based on cost and revenue assumptions that might not hold up. Likewise, property owners can potentially manipulate the expense payment schedule to present an unsustainably high figure.
This is a term mostly used in real estate investing. It effectively describes the priority order of repayment for different types of investors. Especially in large projects for commercial properties (think a giant fulfillment center), there are various investors that could hold different types of debt or different types of equity.
If the project performs as expected when sold, then everyone should profit. If things don’t go quite according to plan and the proceeds fall short of expectations, some investors could end up losing principal. Repayments start from the bottom of the stack (typically senior debt holders). So the higher up an investment is in the stack, the more risk there is.
This concept also exists in the stock market as well. Many public companies have investors that hold bonds, common equity, and preferred equity.
Crop share leases are a financial arrangement relevant to farmland investors. Generally speaking, farmland investors want to own the land without directly doing the farming themselves or managing a crop growing business.
This leads owners to lease the land to operators. Crop share leases are an agreement between the land owner and operator that can allow the owner to share in the profits of the crop harvest.
Crop share leases provide the land owner with potential upside if the market price for a crop increases. The agreement can also require the owner to share in certain operational expenses like fertilizer and can often also allow the operator to pay a lower fixed cash lease payment.
Given the potential benefits to both parties, it isn’t uncommon to see this with permanent crop type farms (e.g. almonds).
D
For investments in SAFEs (Simple Agreement for Future Equity), the discount rate comes into play if a subsequent funding round values the company at less than the valuation cap. In that case, the SAFE will convert to equity based on the valuation with the discount applied.
Let’s look at an example:

In this case the valuation cap is $15M and there’s a discount rate of 10%. That means if the company receives a pre-money valuation of $10M in a subsequent funding round (less than the $15M cap), then the 10% will be triggered. Investors in this SAFE will receive shares based on a $9M valuation ($10M with the 10% discount applied).
Both the valuation cap and discount rate are intended to increase the potential rewards for early investors that are taking on greater risk than those coming in when the company is more established.
Dollar Age is a metric unique to Royalty Exchange. The expectation of future earnings for music royalties is so heavily influenced by how old the song is. Making a valuation assessment for one song can be relatively easy, but what about a catalog with 500 songs all released at different times?
Dollar Age attempts to make it easy to understand the general age of the catalog for valuation purposes. You can read Royalty Exchange’s blog post about the metric for more detail.
F
This is a term typically encountered in real estate, specifically around loans or private credit opportunities.
A lien is a type of legal financing arrangement. Basically, a lien allows a debt holder to take control of a property in order to settle that debt.
A first lien is simply the position of the lien as there can be multiple. The first lien has the best position in the capital stack and is the most likely to see repayment (though that doesn’t make it risk-free). That also means that first lien credit tends to provide a lower yield.
An example of this is on Groundfloor. Groundfloor has first lien debt on the financed properties. That allows them to foreclose on the property if the loan isn’t repaid on time and other terms can’t be worked out. Through this process they attempt to sell the asset and recoup as much investor capital as possible.
Fractional investing is simply by shares or sub-divisions of an asset. This is the norm in the stock market – you buy a share (or a fraction) of equity in Microsoft. You don’t purchase the whole company.
Similarly, things are changing in alternative asset classes to create more opportunities for fractional investments in asset classes that haven’t traditionally had them like contemporary art or farmland.
This is an estimate of what an asset is worth if it were to be sold under the current market conditions. The market for assets is dynamic, so valuations can change greatly over time from that alone.
G
In real estate, the gross yield is basically the revenue generated by a property (before expenses) divided by the property purchase price.
For example, if a property is expected to generate $12,000 per year in rent and the purchase price were $240,000, the gross yield would be 5%. Given this is before expenses and before the mortgage, the property in this example is very unlikely to generate positive cash flow for an investor.
Looking at the gross yield and cap rate can give some at-a-glance understanding to what the economics of a property are. They also provide metrics that can be used to compare properties to each other to help prioritize different opportunities.
K
KYC generally refers to a set of regulations that financial institutions have to follow. This is the reason why banks and investment platforms will ask for a variety of personal details – including your social security number.
Remember that this doesn’t mean that anyone who attempts to gain your personal details is doing so for legitimate purposes.
L
LLCs, or limited liability companies, are a type of corporate structure. The intent with creating an LLC is to have a dedicated legal entity for holding assets or supporting business functions.
In alternatives, LLCs are a common way of fractionalizing an asset. Instead of buying shares of a painting (which you can’t cut into one million pieces and have them still be valuable) you purchase shares of an LLC that owns that painting.
As you might expect from anything related to business and tax law, LLCs are a huge topic that you can delve as deep into as you’d like. There’s no shortage of material.
Liquidity generally refers to the ability to sell assets. Some assets are inherently more liquid (easy to sell) than others. A physical building is inherently more difficult to sell than a share of a publicly traded company.
The Last Twelve Months. This is used in the context of music royalties to describe an assets earnings in the previous year.
Assets are often valued as a multiple of the LTM.
Loan-to-value. This is used mostly in real estate to describe how leveraged a real estate project is. The loan given will be a portion of the total value of the property. The lower the LTV, the greater the margin of safety for the lender.
M
This is the minimum amount of capital required to make an investment.
This may be different from the price per share. For example, shares may be offered for $10, but the minimum investment is $100. That, effectively, means that at least 10 shares need to be purchased to make an investment. After that, additional shares could be added in smaller quantities, such as buying 12 shares for $120 of total investment.
N
Most people are non-accredited investors. To qualify as an accredited investor, you have to pass certain criteria defined by the SEC. See the entry on accredited investors above for more information.
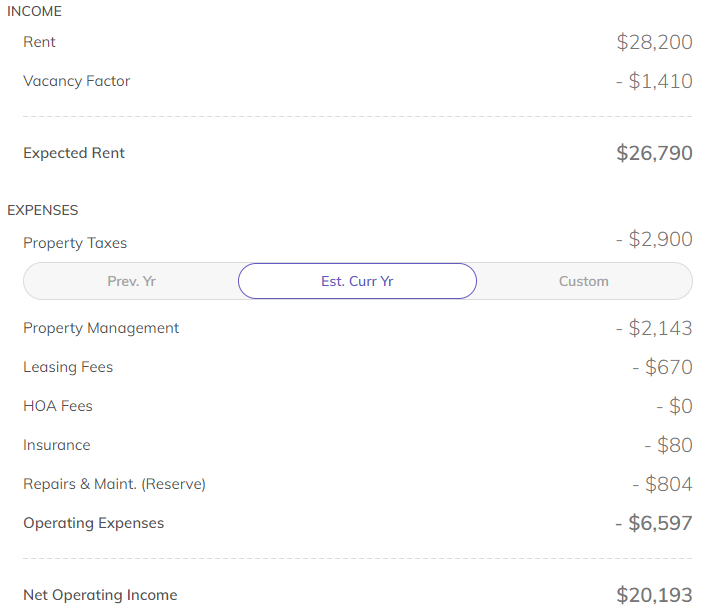
Net Operating Income (NOI). This is a financial calculation often used in real estate. It takes the revenue and subtracts out most operating expenses. Importantly, that does not include the mortgage payment though.
P
These are crops that are not replanted every year. Basically, the opposite of a row crop. Permanent crops typically require several years to grow before they start producing. Once they are mature enough to produce crops, they will continue to produce for years if properly cared for. It is typical for older plants to see a reduction in their crop yield as they age.
Some examples of permanent crops include almond trees and apple trees.
R
Row crops are plants that are planted and harvested within a single year. In the US this is overwhelmingly corn and soybeans.
The short cycle allows farmers optionality in which crop to plant in a given year. That decision can be based on market conditions or crops can be rotated to keep soil healthy. It also provides some isolation from the impacts of a year of bad weather. On the flip side, row crops are commodities that often sell for a lower profit.
Simply put, a royalty is basically an agreement to pay someone for the use of their thing. That thing can vary significantly and could even include the use of someone’s face or name on a product or service offering.
In alternatives, we most often see this in the context of music. Whenever you stream a song from a platform like Spotify, royalties are accrued for the rights holders of that song.
The legal and financial structures of royalties typically allow the rights to receive the royalty payments to be sold and traded. And thus investments can be made by purchasing these rights.
S
This is a term typically encountered in real estate, specifically around loans or private credit opportunities.
A lien is a type of legal financing arrangement. Basically, a lien allows a debt holder to take control of a property in order to settle that debt.
A second lien refers to the position of the lien in terms of repayment. A second lien will always receive repayment after a first lien. This makes them higher risk investments than first lean debt, but they often offer higher potential yield as a reward for the heightened risk.
A secondary market allows assets to be bought and sold amongst investors. Secondary markets are important because they offer investors an avenue to exit their investment before a liquidity event – such as the investment property being sold.
Not all investment platforms offer secondary markets. The markets also typically come with trading fees and can suffer from low liquidity.
Series LLCs are an extension of limited liability companies. In this structure, a “parent” LLC can have multiple “child” LLCs called series. The intention is for each series to still function like an LLC – separate assets, separate members, and separate liability.
The series structure is used by some investment platforms for their offerings. This structure is presumably used because it can be easier to administer.
A Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE) is kind of like an IOU for equity – with certain conditions attached. The SAFE will convert to equity if there is a future priced round where the company sells equity. The valuation cap and discount affect the math of how SAFE investors receive their equity.
Being able to issue the IOU makes it much simpler for startups looking to raise money. It also comes without the burden of interest payments. Since startups may be challenged for revenue in the earliest days, this is a huge benefit for them.
For investors, SAFEs are mostly more risky than alternative structures like convertible notes. Some venture capitalists simply refuse to invest in SAFEs for this reason. However, the availability of SAFE agreements lowers the barrier for companies to raise funds. This can also increase the amount and variety of opportunities available to investors.
A single family home is a type of residential real estate property. This is in contrast to commercial properties (like offices) and multi-family homes (like duplexes or apartment buildings). Single family homes are typically individual buildings that share no walls with other dwellings.
In recent years, these types of properties have been a focus for real estate investors.
V
If a SAFE investment converts into equity, the valuation cap is the maximum valuation the conversion will occur at. For example, if there is a valuation cap of $100M, then investors of the SAFE will receive shares based on the $100M valuation even if the next funding round valued the company at $1B.
Of course, the valuation cap only comes into play if a future funding round values the company at more than the SAFE’s cap. In other words, a valuation cap of $100M is irrelevant if the company is only valued at $50M in the future funding round. In that case, the discount rate from the SAFE may come into play.

